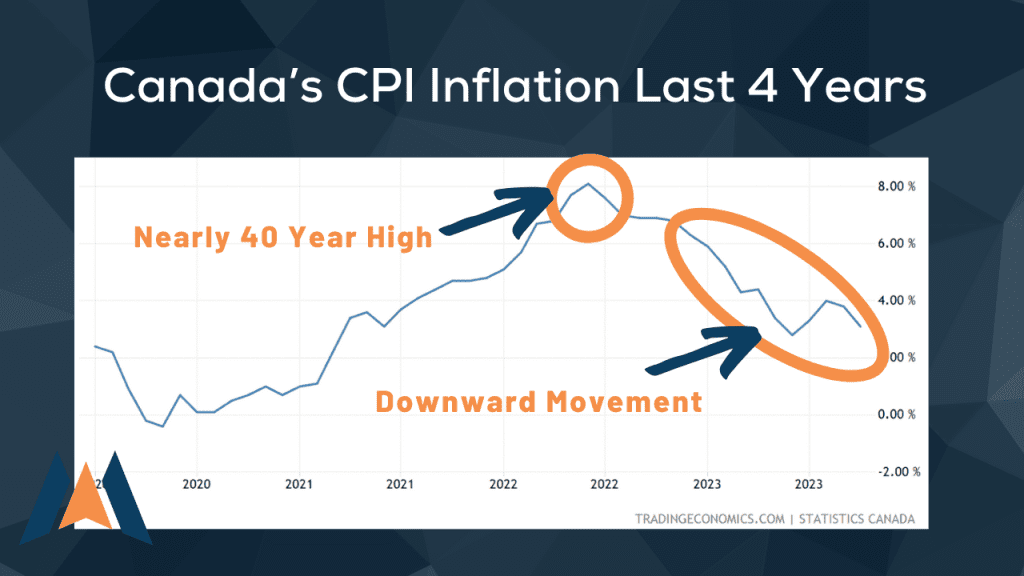
Recent developments from the Bank of Canada indicate a significant shift in its monetary policy. The central bank’s decision to maintain the policy rate suggests a potential halt to the rate hike cycle. This move, influenced by factors like subdued inflation and increasing unemployment, hints at a more cautious approach moving forward.
Balancing Inflation and Growth
Although rate hikes have paused, the Bank of Canada remains vigilant about inflationary pressures. The central bank’s cautious statements aim to temper public expectations while carefully managing long-term interest rates to support economic stability.
Housing and Economic Outlook
The real estate and mortgage sectors face a complex period ahead. The current market dynamics, characterized by increasing supply and declining sales, signal a buyers’ market with restrained activity. This scenario might require several months to reach equilibrium.
Comparing today’s market conditions to the 1991 recession, the current situation, though less severe, presents its unique challenges. Price pressures, especially in the condominium segment, are expected due to rising supply.
The recent surge in interest rates poses challenges for Canadian borrowers, particularly at renewal. Lowering rates in 2024 could mitigate potential increases in delinquency rates, making the economic adjustment more manageable.

Economic Forecast for 2024
The outlook for Canada’s economy in 2024 is cautiously optimistic. Despite current downturns in consumer spending and the housing market, there are positive signs, like the normalizing labour market, indicating potential improvement in the latter half of the year.
Global Influences: The Role of the US Federal Reserve
The US Federal Reserve’s monetary policies have a consequential impact on Canada. The Fed’s cautious stance on rate cuts in 2024, influenced by inflation trends, is a critical factor for the Canadian economy and the Bank of Canada’s future decisions. When there is a differential between the Bank of Canada and the US Fed’s rate, it impacts the exchange rate. When the Canadian dollar is weak against the US Dollar, that adds to inflationary pressure.
In summary, while the Bank of Canada’s aggressive rate-hiking approach appears to be on pause, the Canadian economy, particularly the housing market, faces significant challenges ahead. The central bank’s strategy in the coming months will be crucial in navigating these challenges, with an eye on both domestic economic conditions and international monetary trends, especially those set by the US Federal Reserve.